What is Metal Injection Molding (MIM)
Metal injection, molding is a kind of metal manufacturing technology. That utilizes metal powders, combined with organic binders, using injection molding technology, to produce highly complex structural metal components. Parts are subsequently processed and centered to yield high strength, intricately shaped.
MIM Powder Market
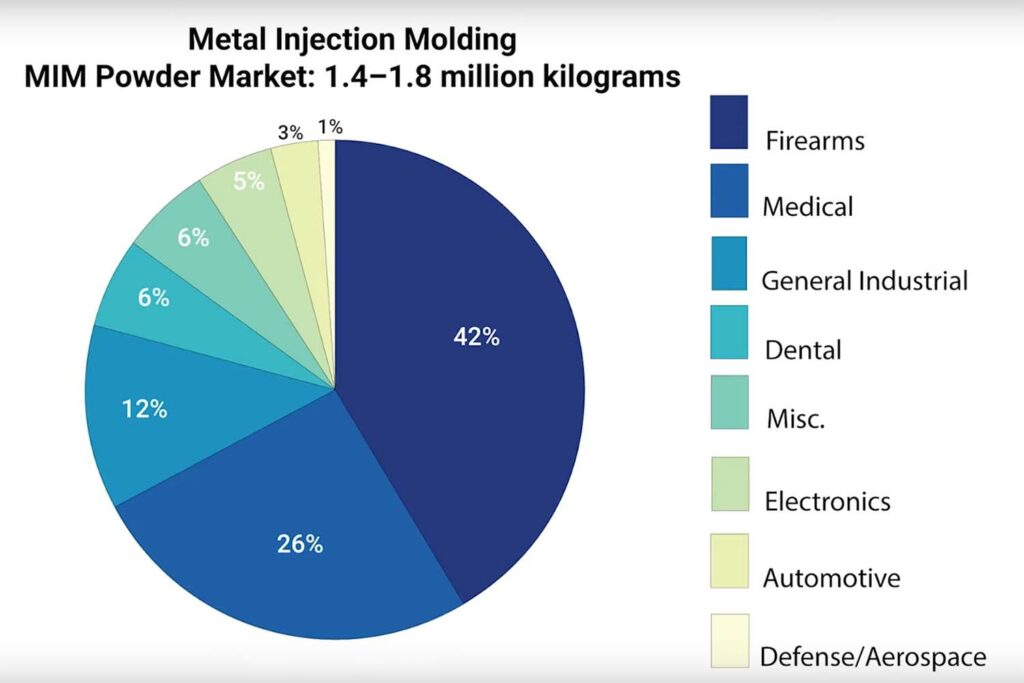
Components produced by metal injection molding are used by medical and dental markets, General, and industrial markets. Firearms, automotive electronics, miscellaneous other users Aerospace, and Automotive. We see here that medical dental and general industrial, and Firearms are the dominant users of metal injection molded components.
So one of the questions we asked, is, is my part a good fit for the MIM process.
Four considerations when choosing MIM Process
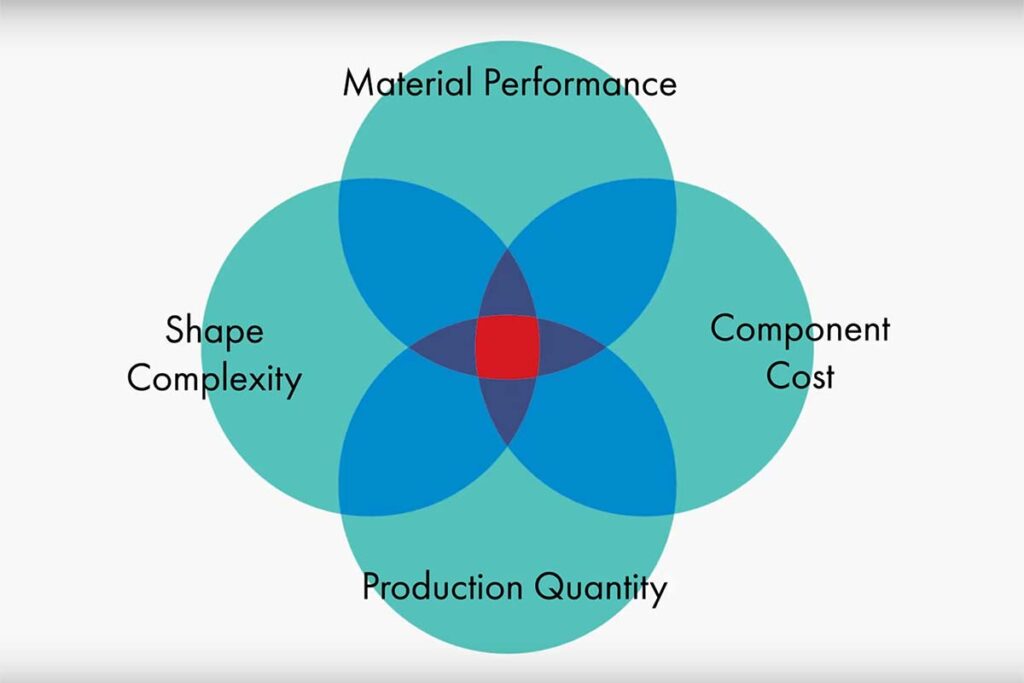
And here we see in this model, material performance, component cost, production quantity, and shape complexity. The closer we can get to the intersection of these four circles, the better the application is for metal injection molding.
Steps by steps metal Injection Molding Process
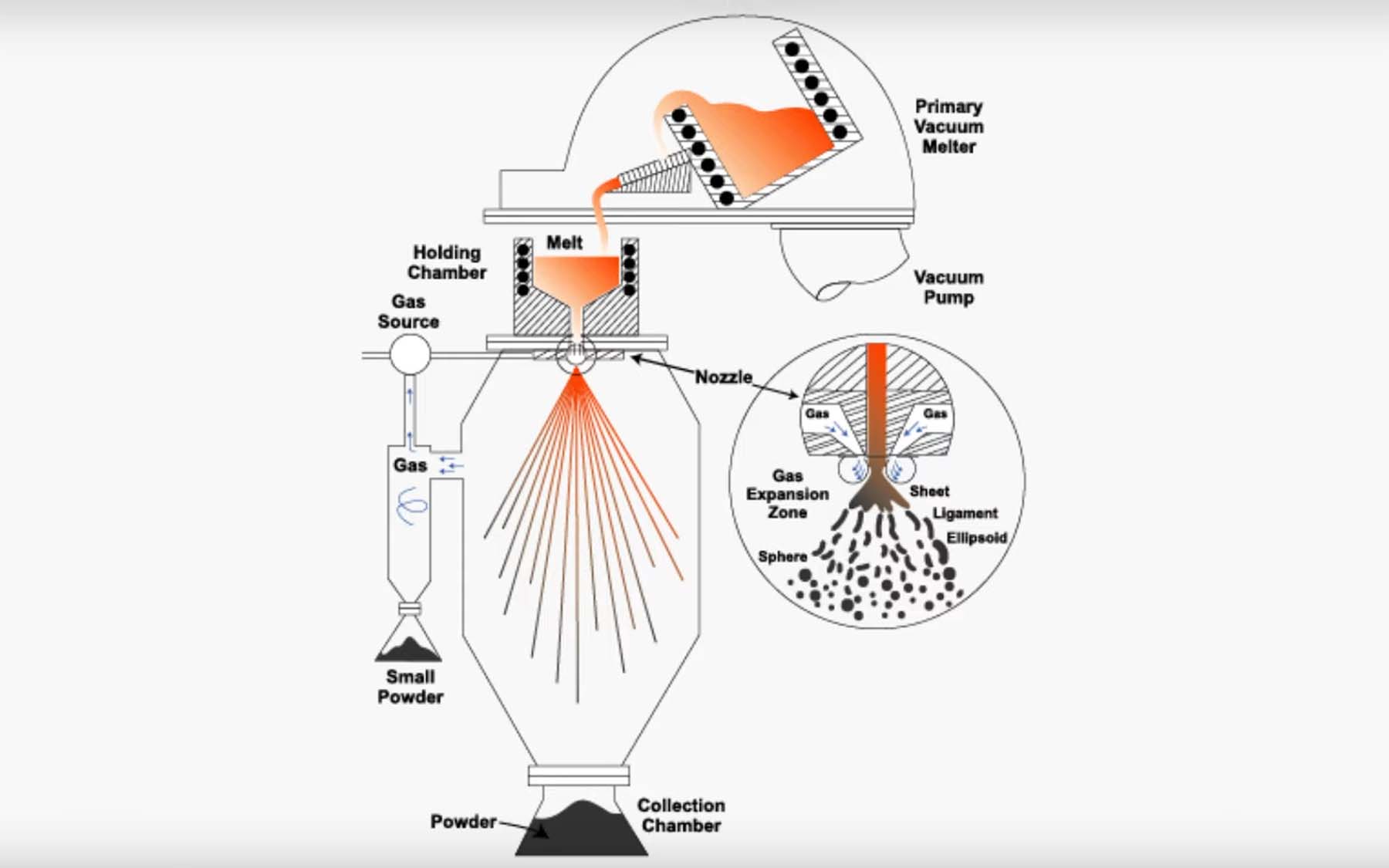
Powders used in the metal injection molding process are produced from gas atomization. Here we see a model of the gas atomization process. We start with molten metal, the material is then poured into a holding chamber. And from the holding chamber, it is discharged into the atomization area, where the molten metal is hit with high-pressure inert gas to produce metal powders.
It is then subsequently processed and finished for use , and you can see the spherical nature of the gas atomized powders. This is ideal for metal injection molding, because they have a low coefficient of interparticle friction.
Metal injection molding process starts with metal powder and binders. Those binders are then compounded into a paste like material which is turned into small pellets. This becomes the feedstock that is used in the metal injection molding process. Components are molded in a metal injection molding press from there, that binders are removed in a what we call a lady binding process or dewaxing after the D binding process. The components are centered at elevated temperatures, typically in the 20, 350 degrees F or higher in a protective environment or in some cases in a vacuum and then post sintering process. Cesare performed as necessary. The gas atomized powder. It’s used in metal injection. Molding is put into the feed stock granules. You can see on the right. The feedstock is then fed into the molding press, or the components are molded under high pressure.
After molding. The binder is removed through the D, binding process, the typical binders of Ali oxy. Methylene, or Palm polyethylene or polypropylene, which are synthetic or natural waxes. And stearic acids are also used is binders. There’s a catalytic D binding process, which is an acidic gaseous atmosphere. That’s used to remove the Palm binders as well. We can also use thermal or solvent de binding using acetone heptane or an aqueous solution after d. Components are then centered either in a pusher type continuous, sintering, furnace or in a batch type sintering, furnace at elevated temperatures either in vacuum or protective atmosphere.
As you can see, in metal injection molded components. We often times, see, as much as 15 to 20 percent shrinkage. After the sintering process, some common MIM applications are firearms here. We see an example of some memcache. Components that were used as Smith & Wesson rifle.
This is an example of a sound tube that’s used in a hearing aid, made from 316 stainless steel and we see the orthodontic appliances using a metal injection.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.